Gallery of Physical Molecular Models
Phospholipids with Other Molecules

Phospholipids with Other Molecules
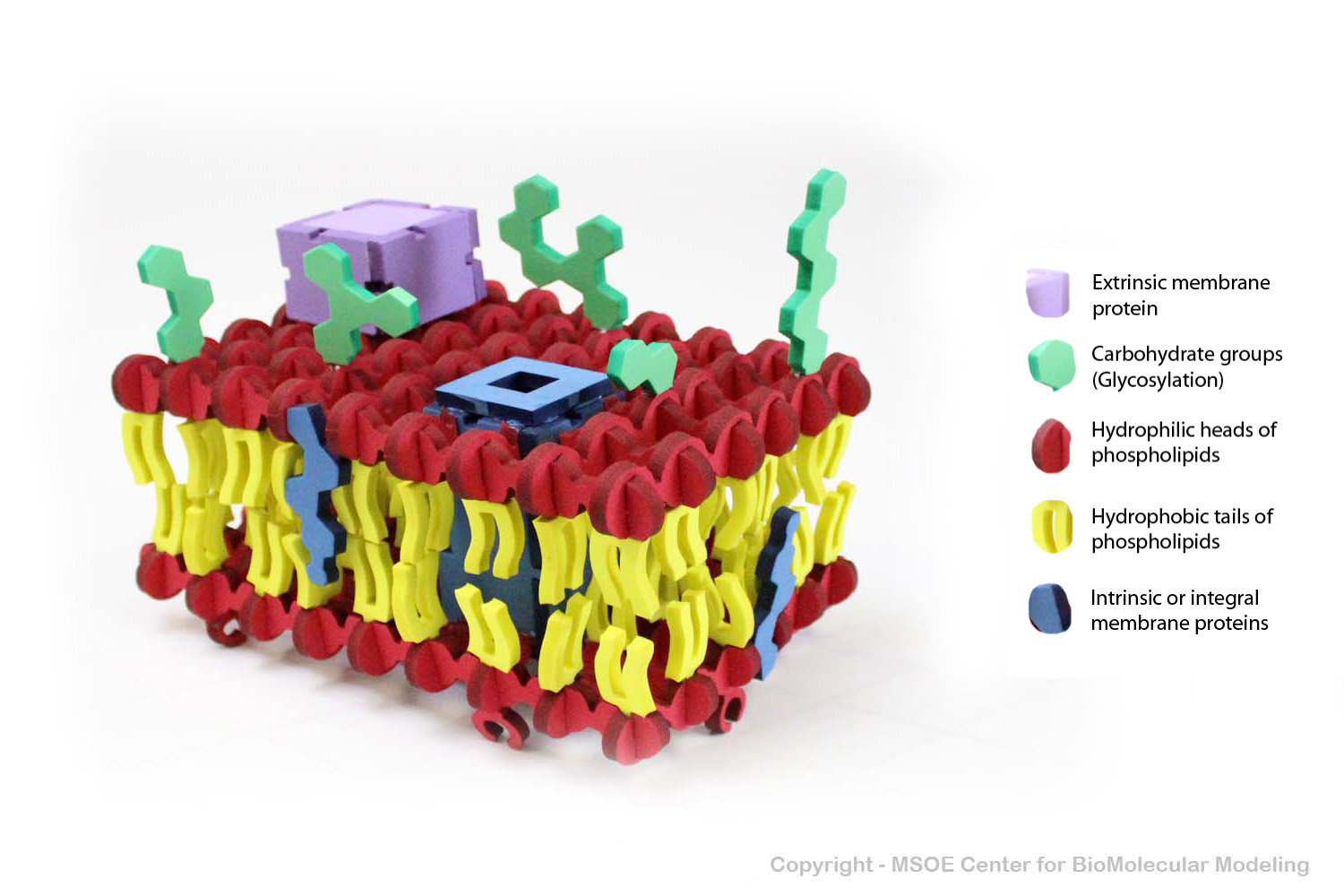
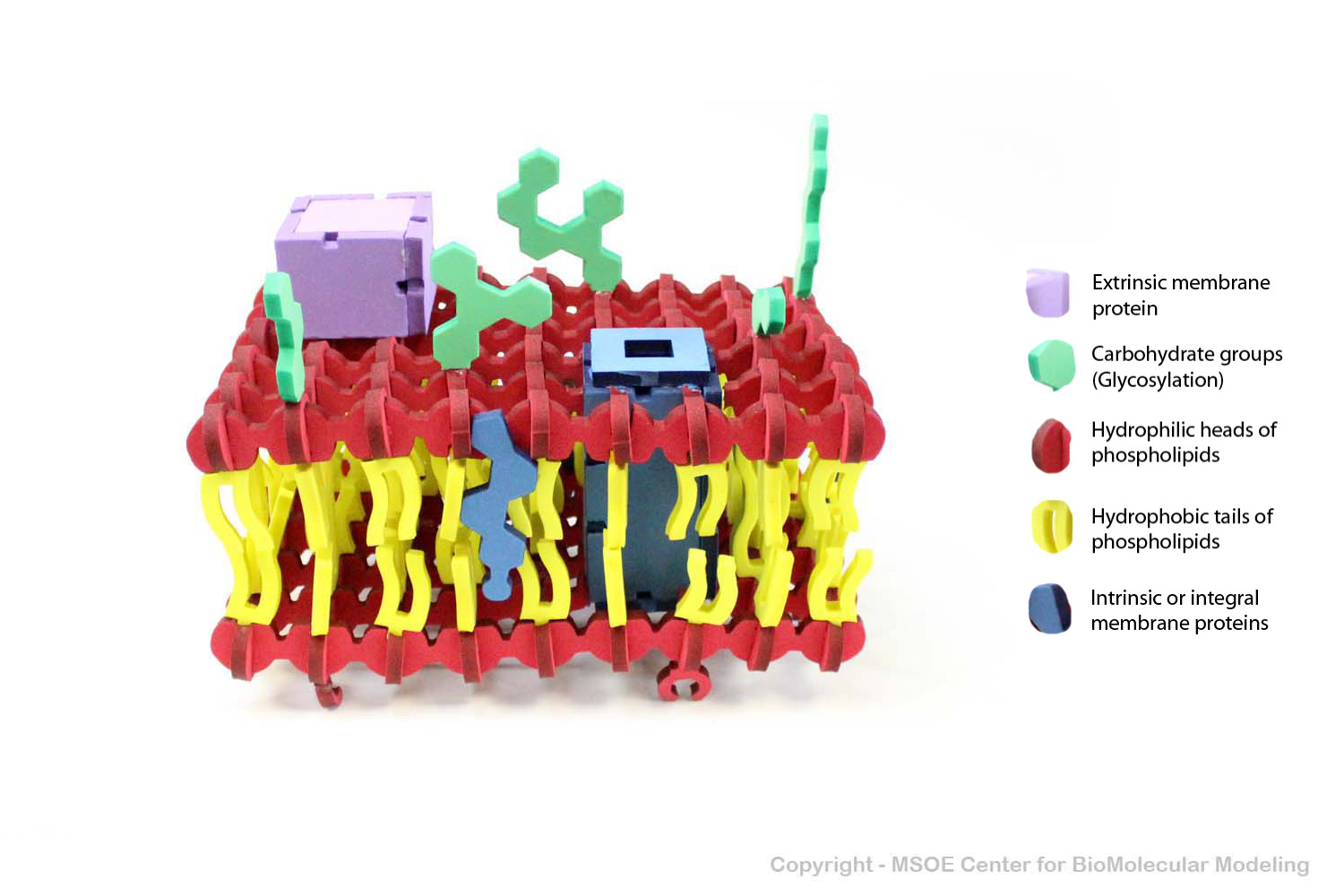

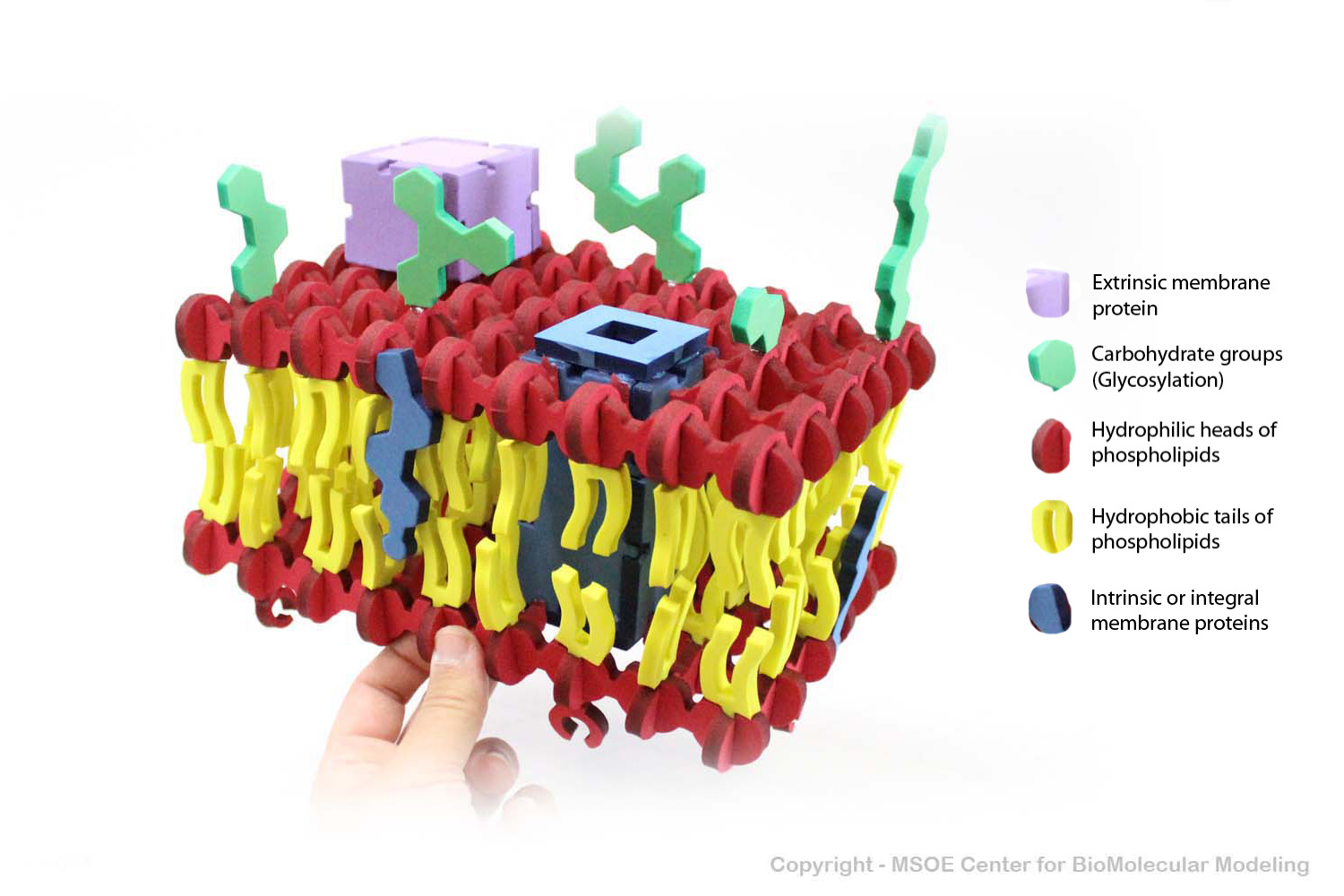


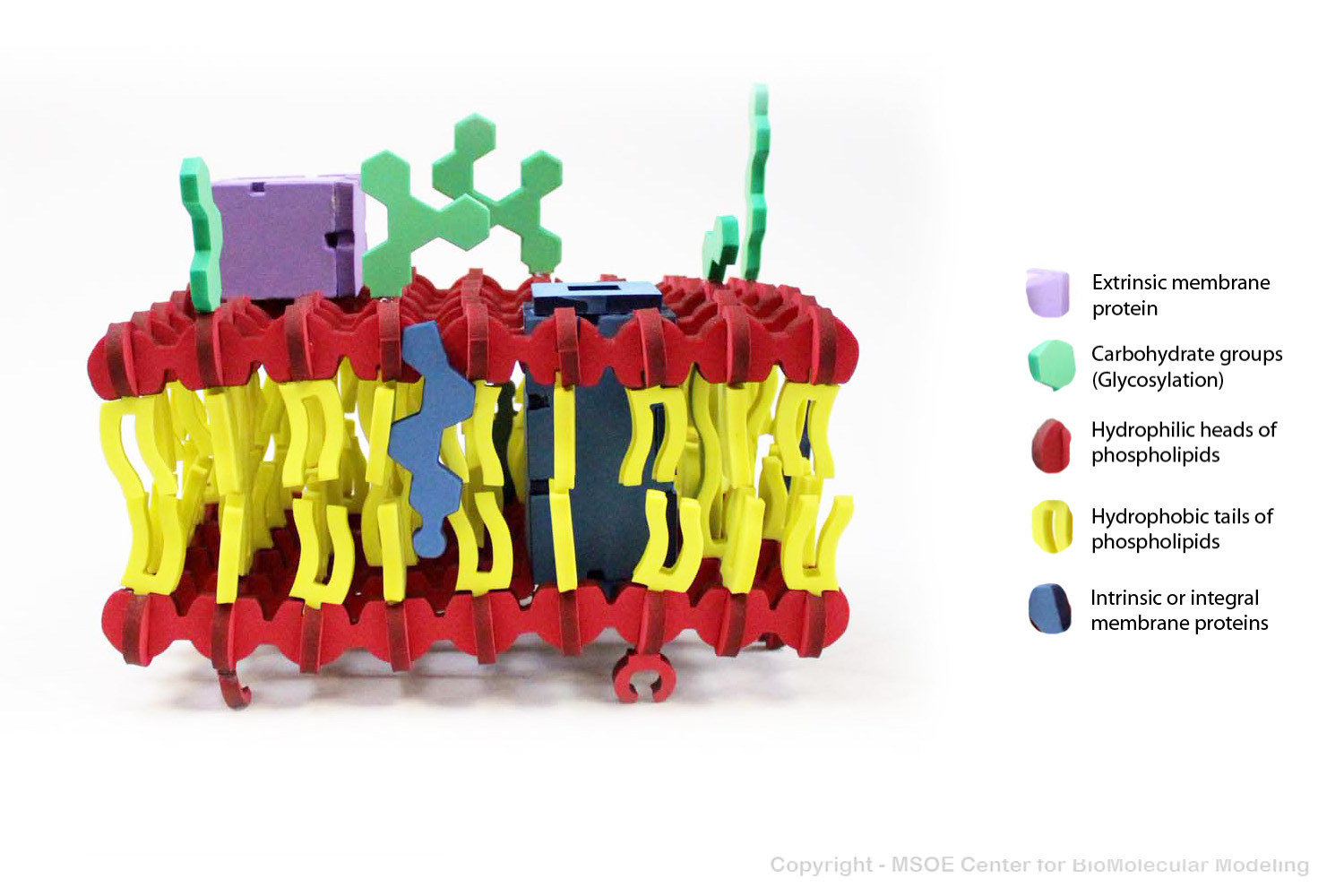
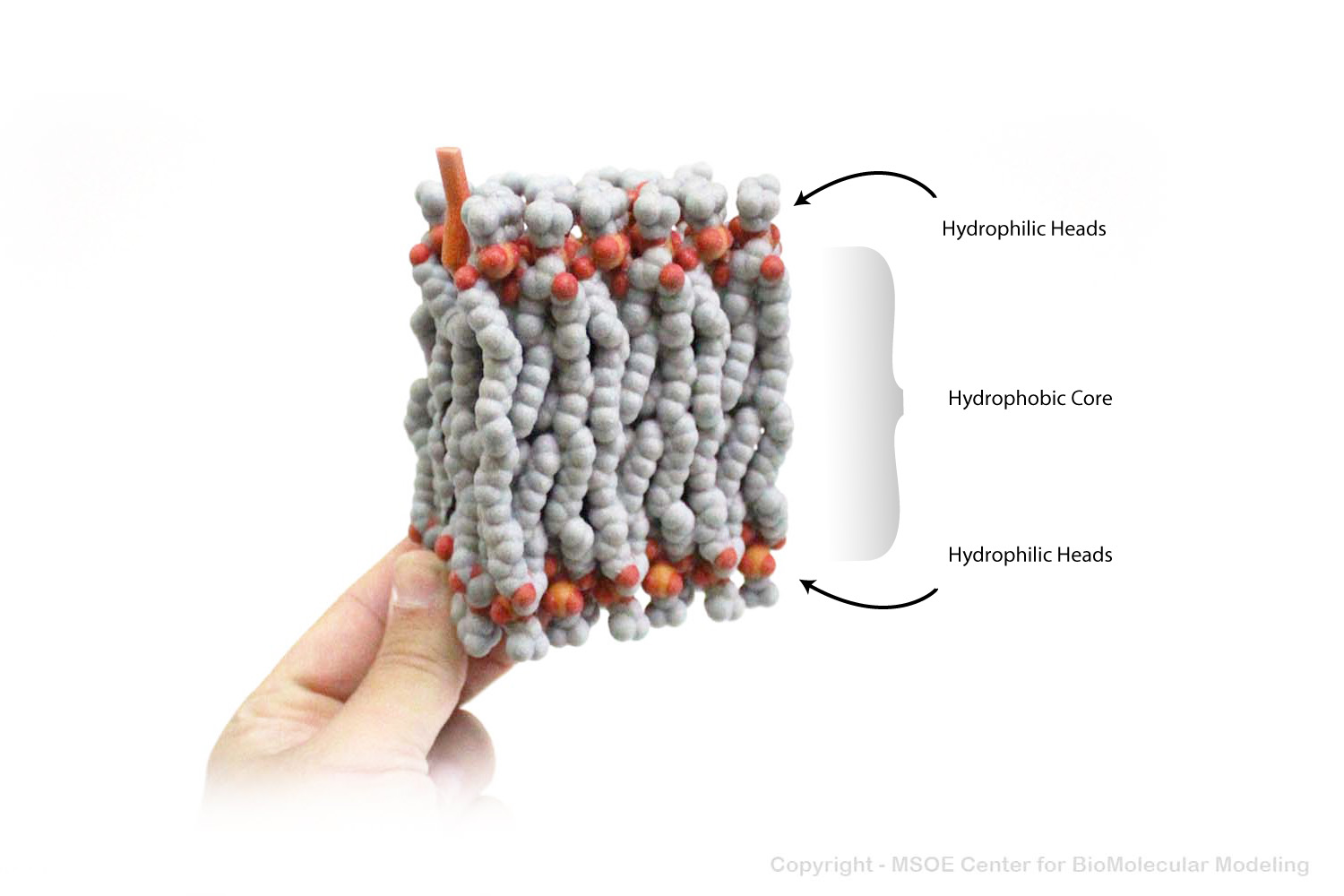

Multiple phospholipids can aggregate into a lipid bilayer, with hydrophobic tails in the middle of the bilayer and hydrophilic heads on the outside of the bilayer. Other molecules, such as protein and glycans decorate the bilayer.

Multiple phospholipids can aggregate into a lipid bilayer, with hydrophobic tails in the middle of the bilayer and hydrophilic heads on the outside of the bilayer. Other molecules, such as protein and glycans decorate the bilayer.

Multiple phospholipids can aggregate into a lipid bilayer, with hydrophobic tails in the middle of the bilayer and hydrophilic heads on the outside of the bilayer. Other molecules, such as protein and glycans decorate the bilayer.

Multiple phospholipids can aggregate into a lipid bilayer, with hydrophobic tails in the middle of the bilayer and hydrophilic heads on the outside of the bilayer. Other molecules, such as protein and glycans decorate the bilayer.
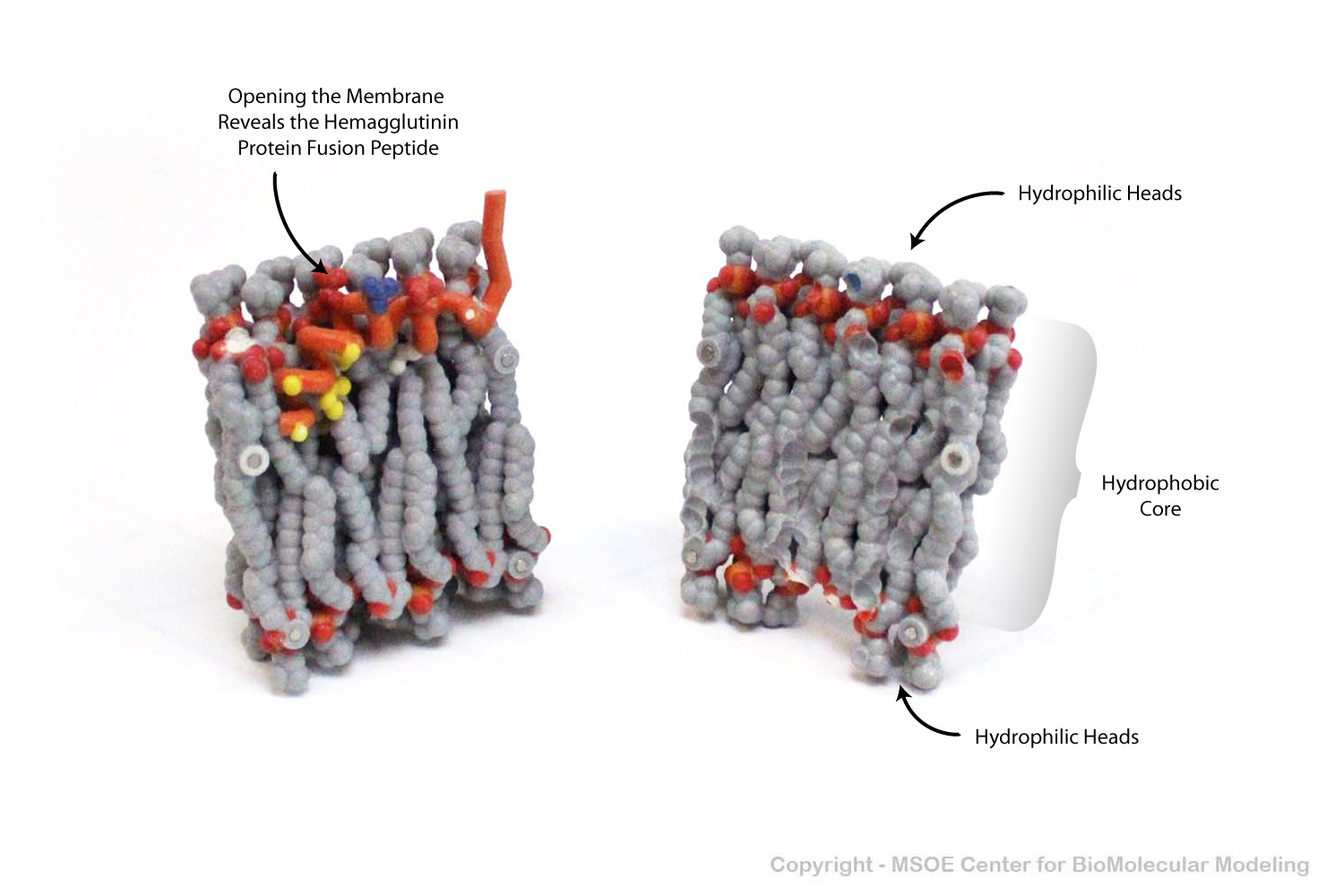
The hemagglutinin protein found on the surface of the influenza flu virus contains a specialized fusion peptide that embeds itself in the phospholipid bilayer of the host cell it is attacking.
The hemagglutinin protein found on the surface of the influenza flu virus contains a specialized fusion peptide that embeds itself in the phospholipid bilayer of the host cell it is attacking.
The hemagglutinin protein found on the surface of the influenza flu virus contains a specialized fusion peptide that embeds itself in the phospholipid bilayer of the host cell it is attacking.
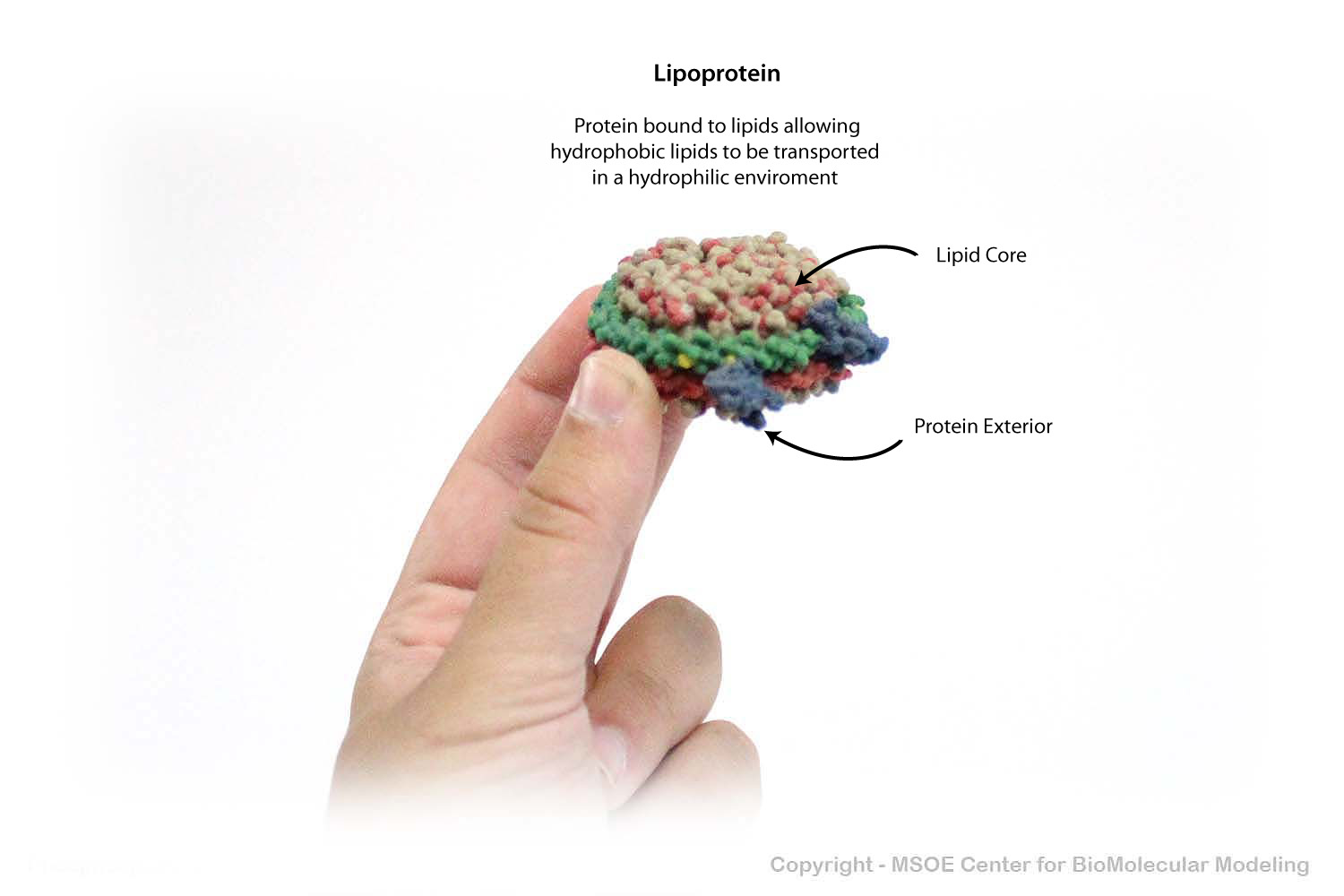
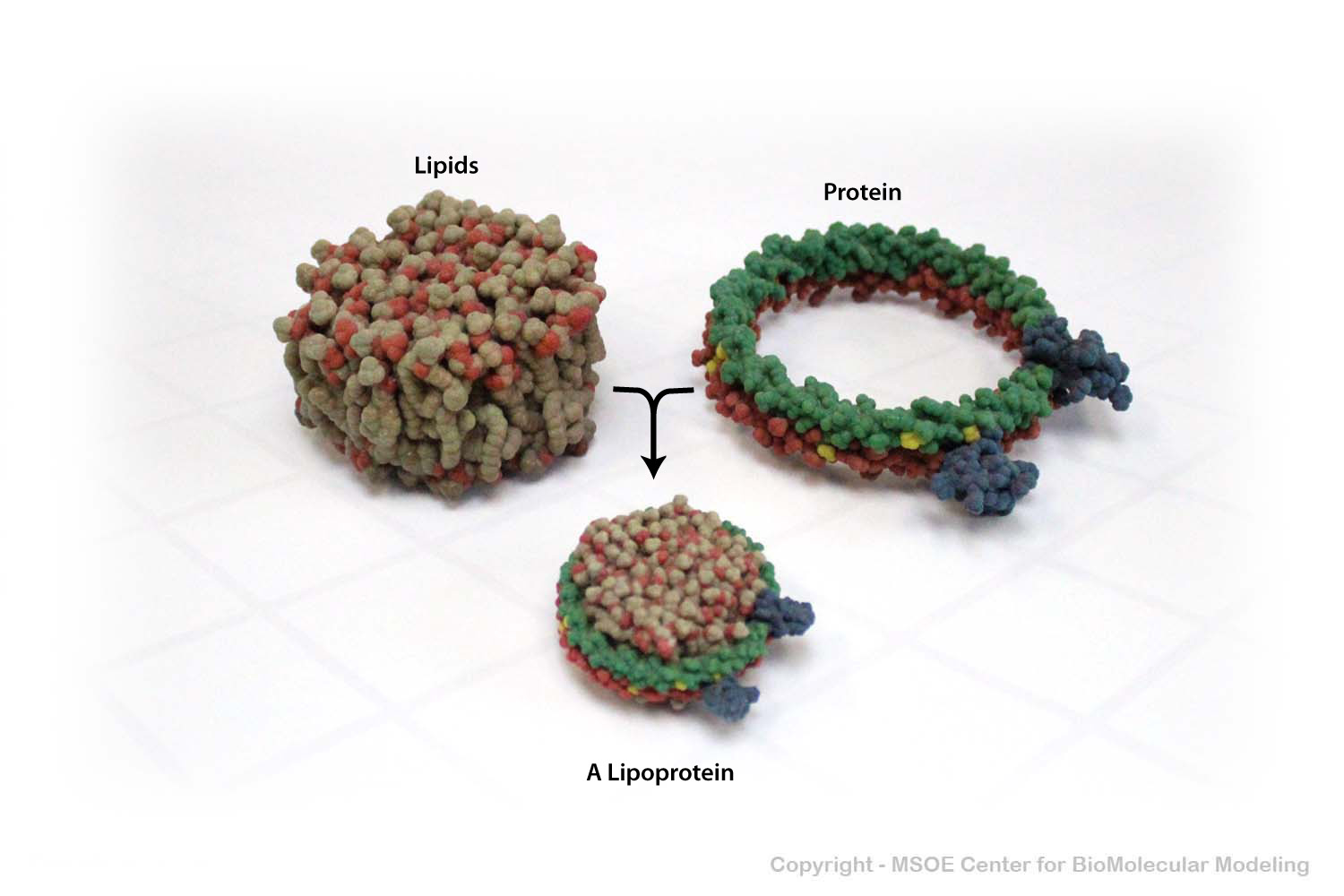
To be safely transported throughout the cell, lipids are bound by lipoproteins, which shelter the hydrophobic tails of the lipid aggregate to protect it from the aqeous environment of the cytoplasm.
To be safely transported throughout the cell, lipids are bound by lipoproteins, which shelter the hydrophobic tails of the lipid aggregate to protect it from the aqeous environment of the cytoplasm.
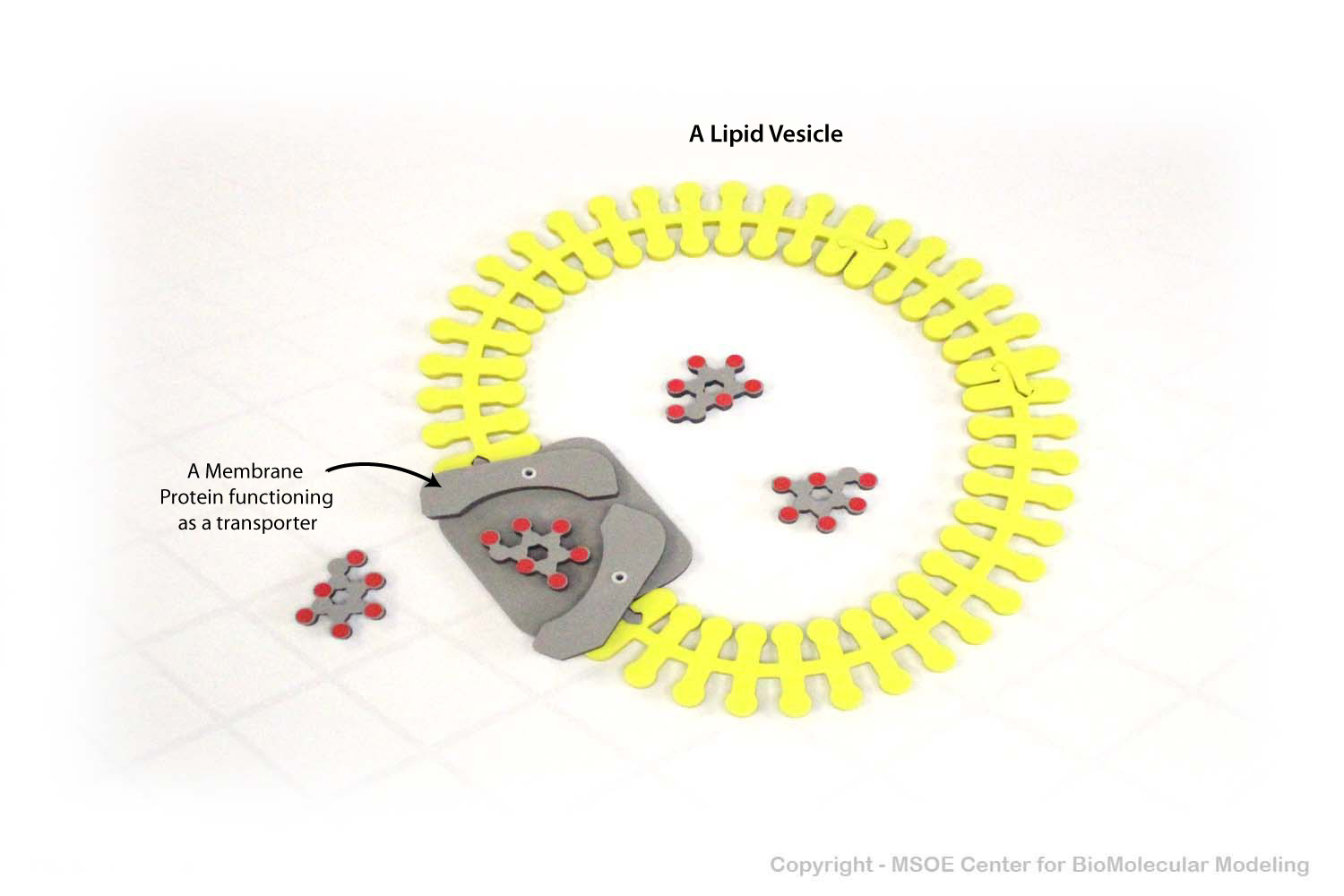
Glucose transport proteins (GLUTs) are stored in lipid vesicles, where they can allow glucose molecules to move across the lipid bilayer.
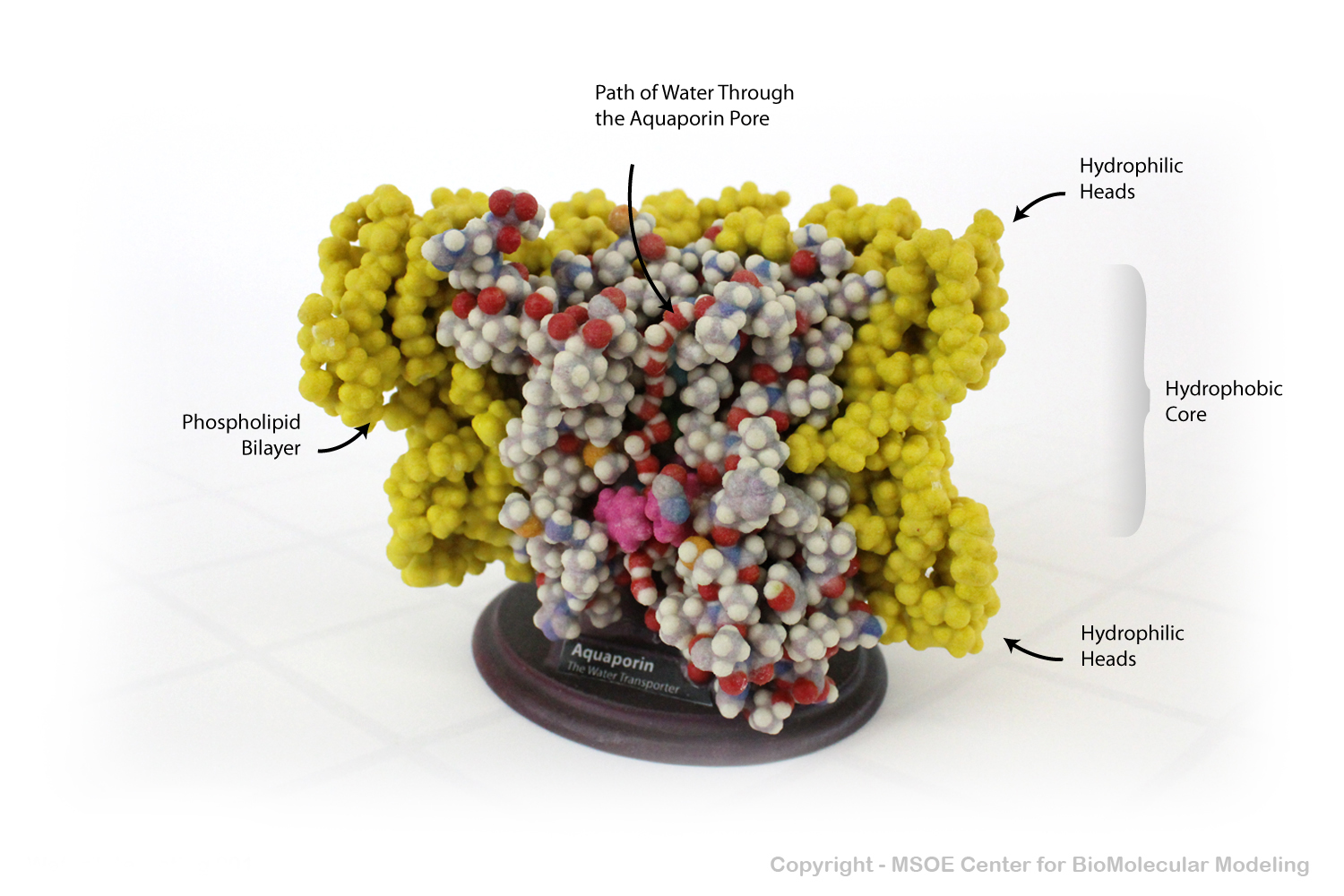
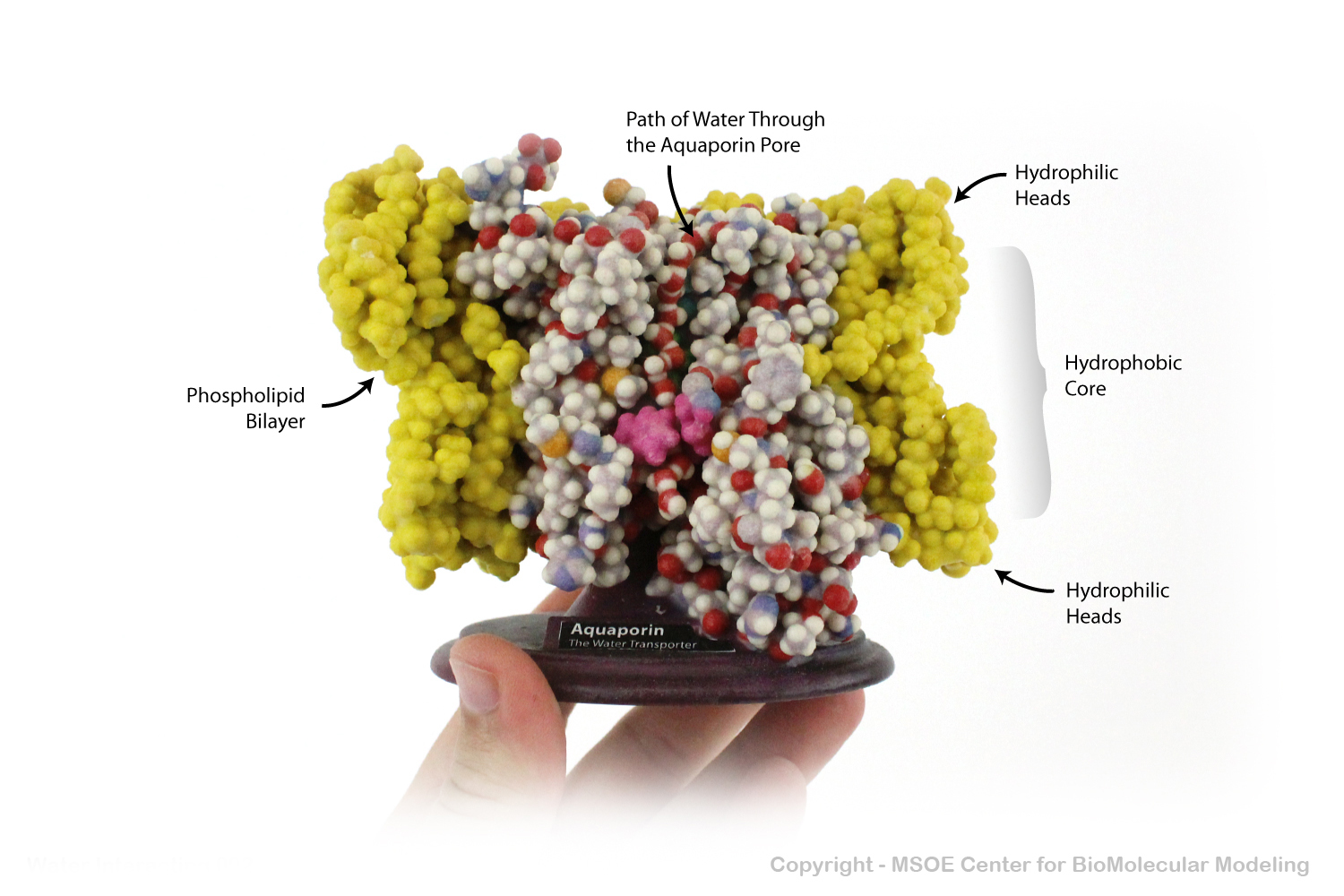
Aquaporin is a highly selective protein channel that allows water molecules to cross a phospholipid bilayer (membrane). This model shows a cross section of the aquaporin protein, revealing the path of the water molecules through the pore.
Aquaporin is a highly selective protein channel that allows water molecules to cross a phospholipid bilayer (membrane). This model shows a cross section of the aquaporin protein, revealing the path of the water molecules through the pore.
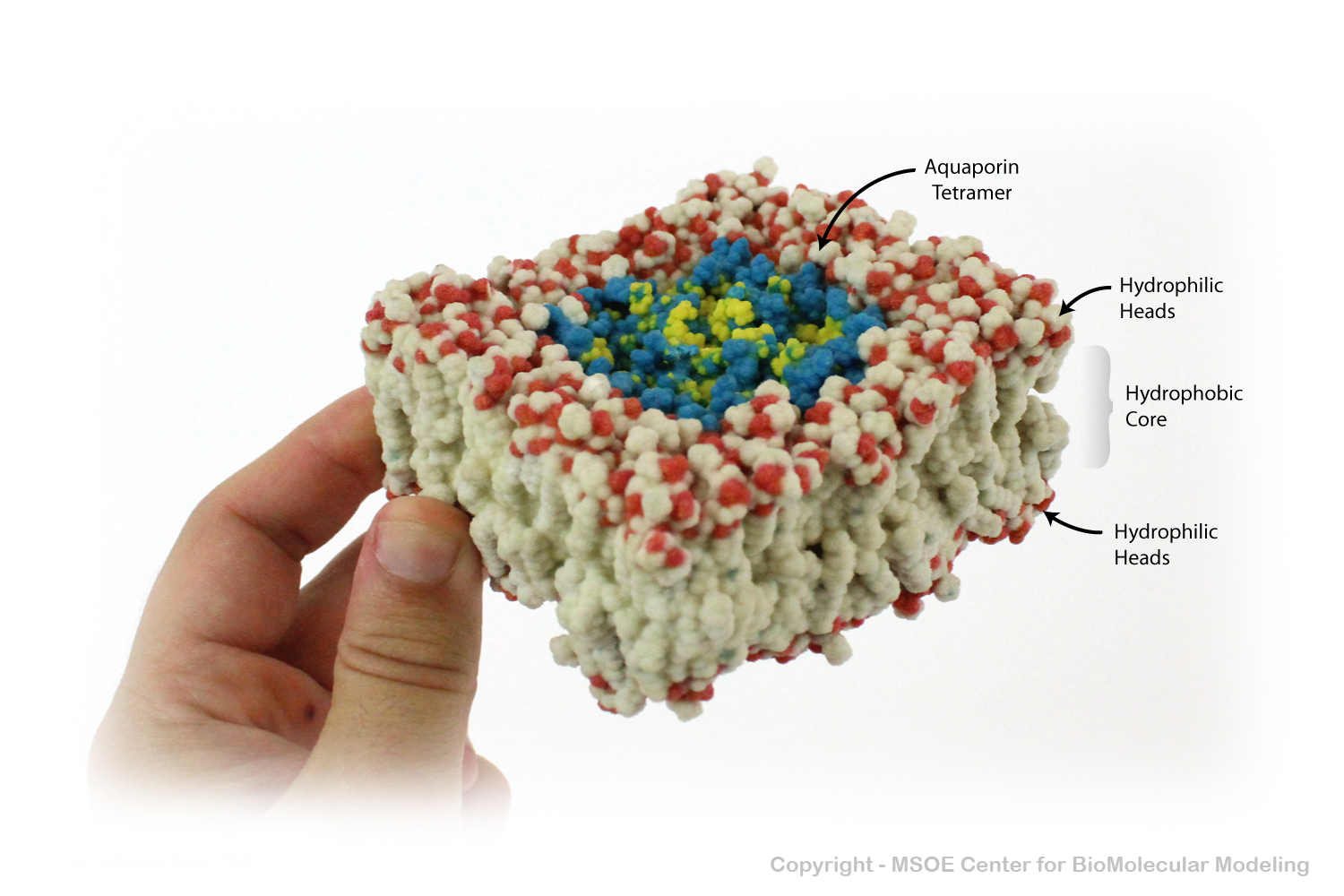
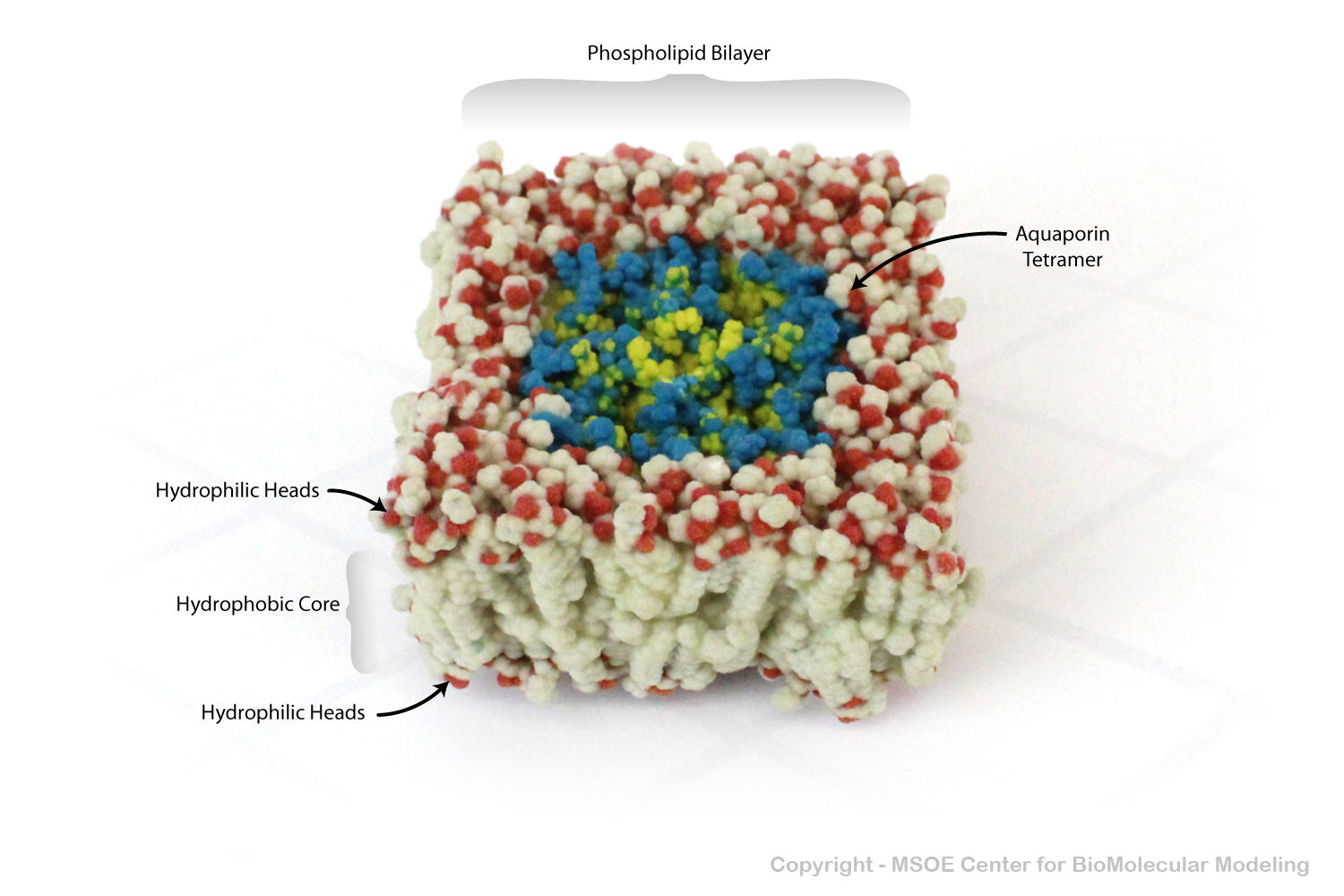
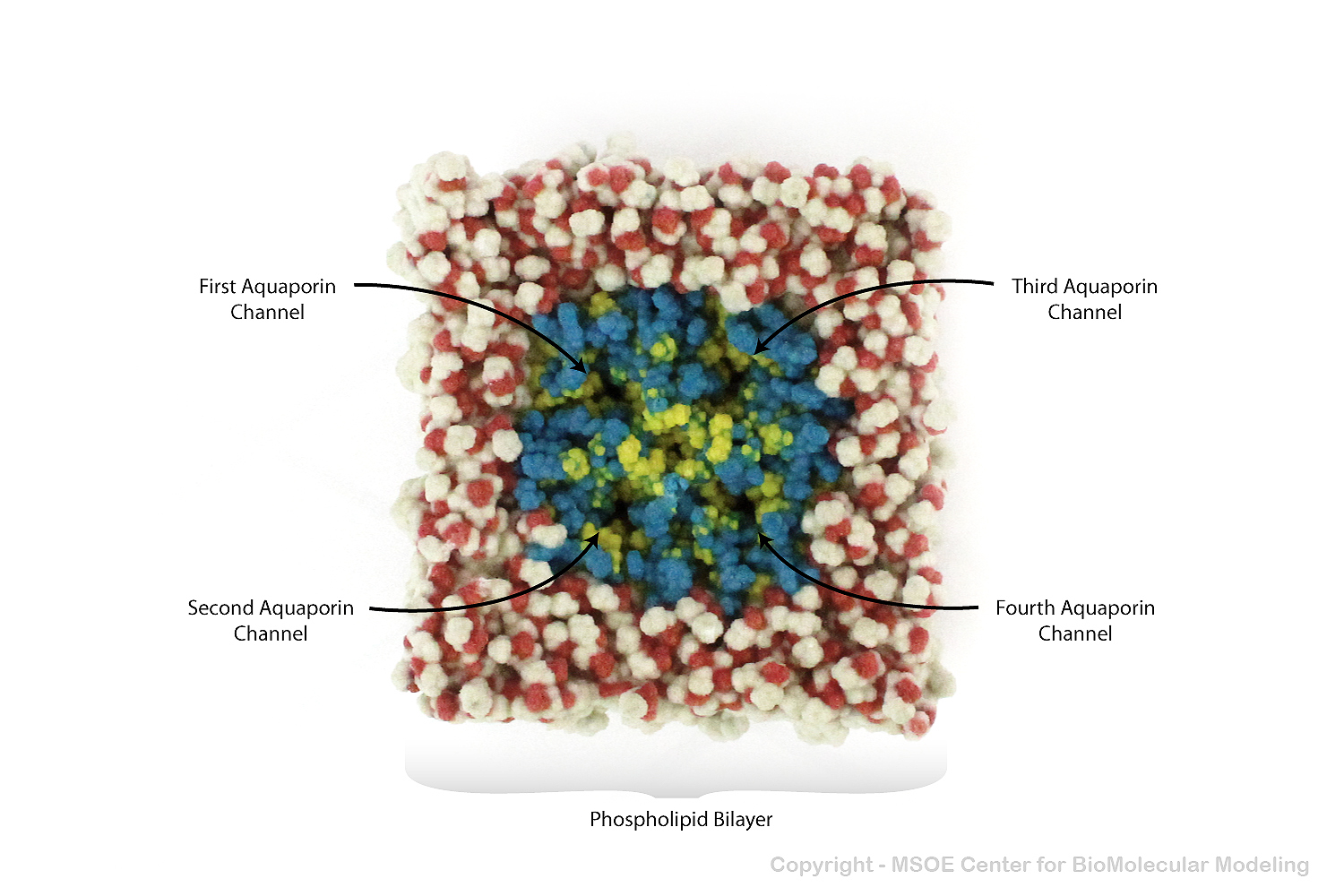
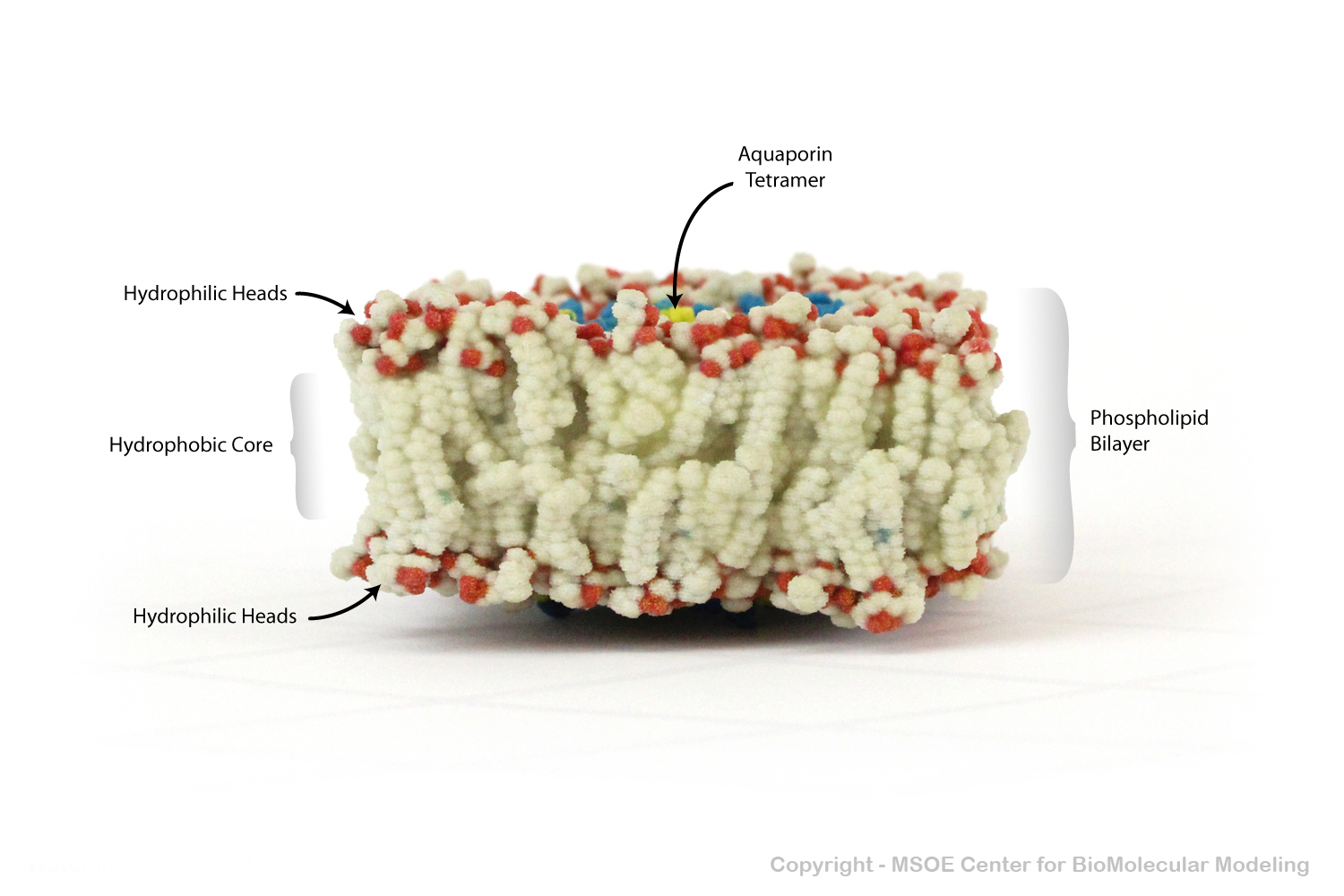
Aquaporin is a highly selective protein channel that allows water molecules to cross a phospholipid bilayer (membrane). This model shows an aquaporin tetramer, comprised of four identical aquaporin protein chains, embedded in a membrane.
Aquaporin is a highly selective protein channel that allows water molecules to cross a phospholipid bilayer (membrane). This model shows an aquaporin tetramer, comprised of four identical aquaporin protein chains, embedded in a membrane.
Aquaporin is a highly selective protein channel that allows water molecules to cross a phospholipid bilayer (membrane). This model shows an aquaporin tetramer, comprised of four identical aquaporin protein chains, embedded in a membrane.
Aquaporin is a highly selective protein channel that allows water molecules to cross a phospholipid bilayer (membrane). This model shows an aquaporin tetramer, comprised of four identical aquaporin protein chains, embedded in a membrane.
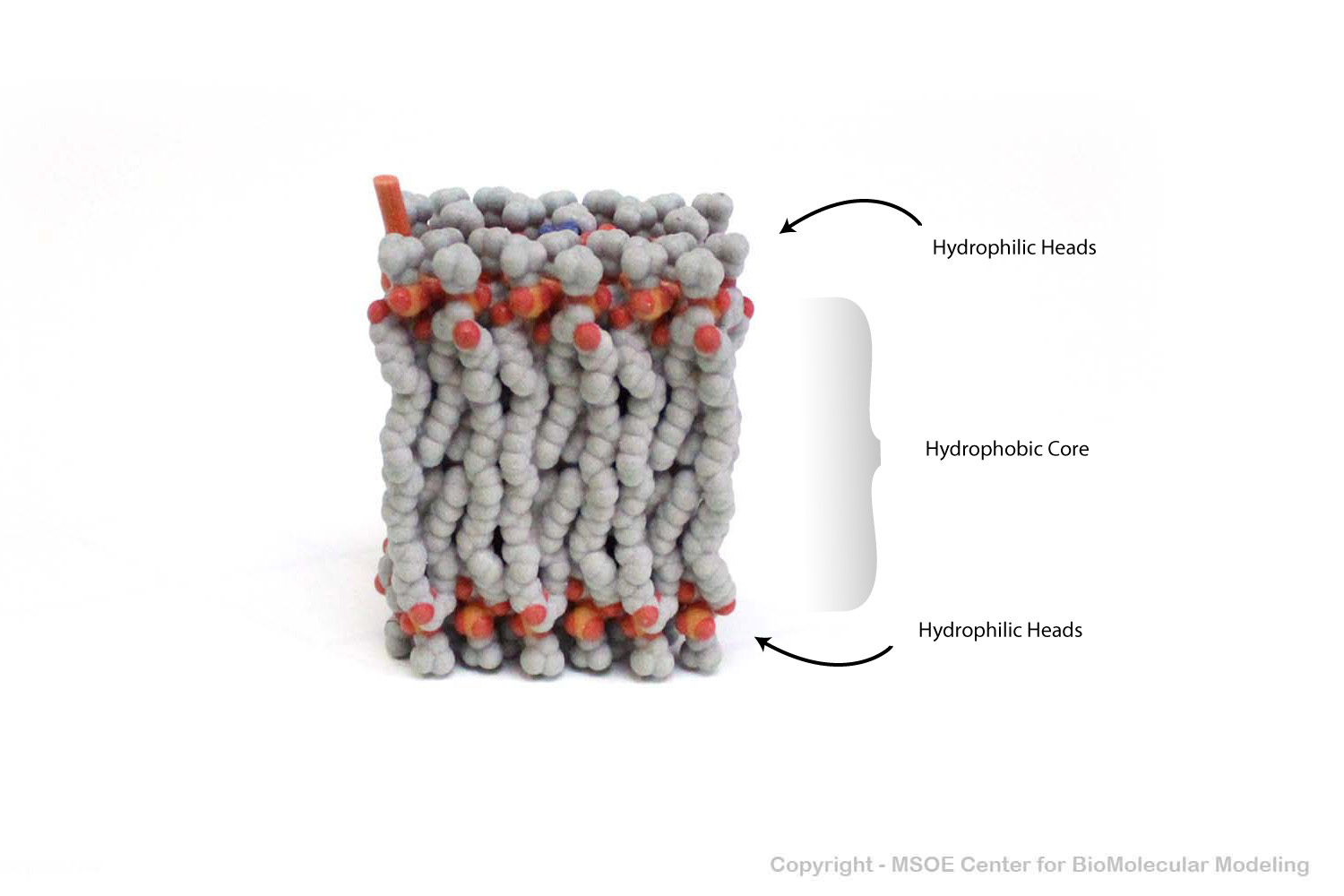
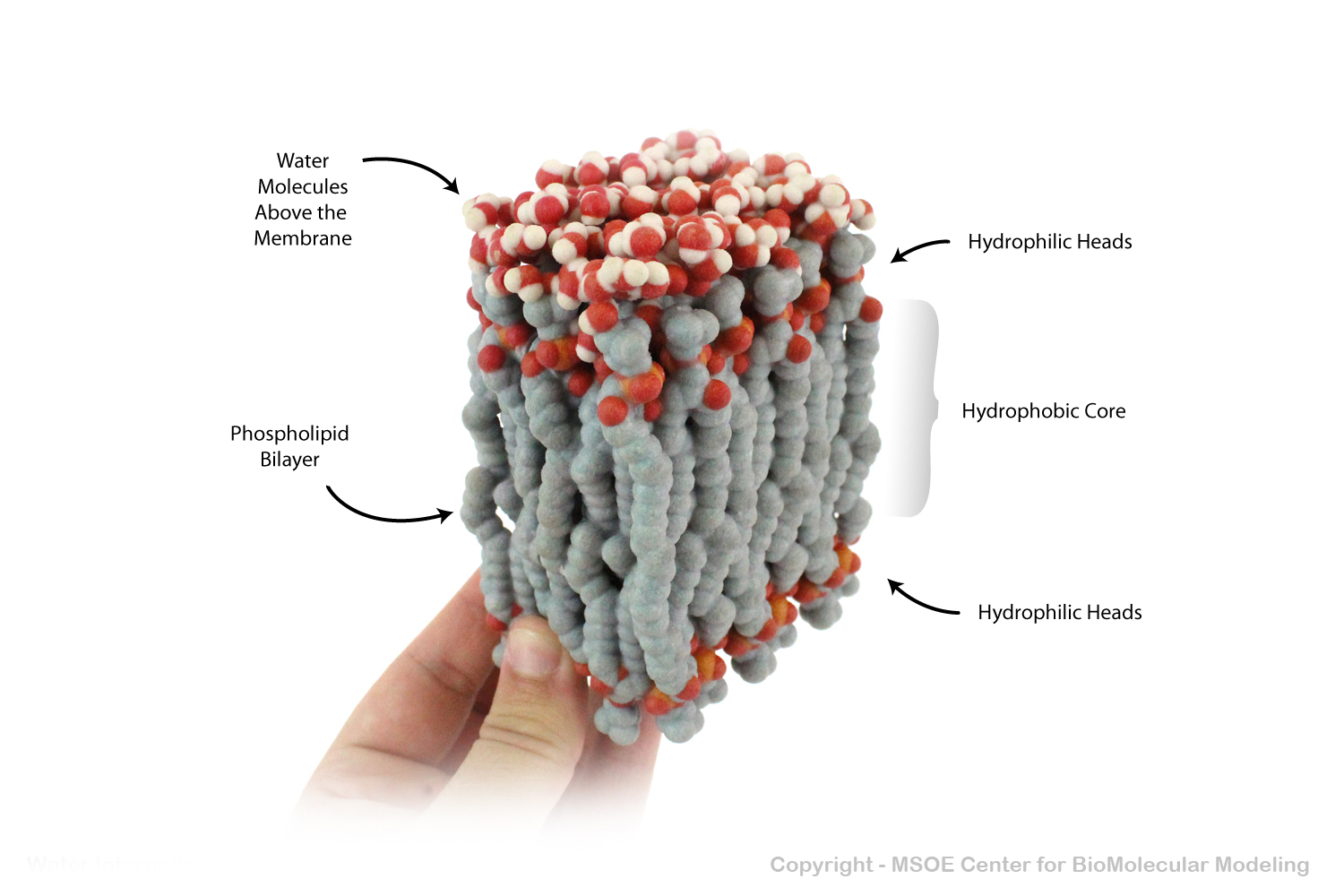
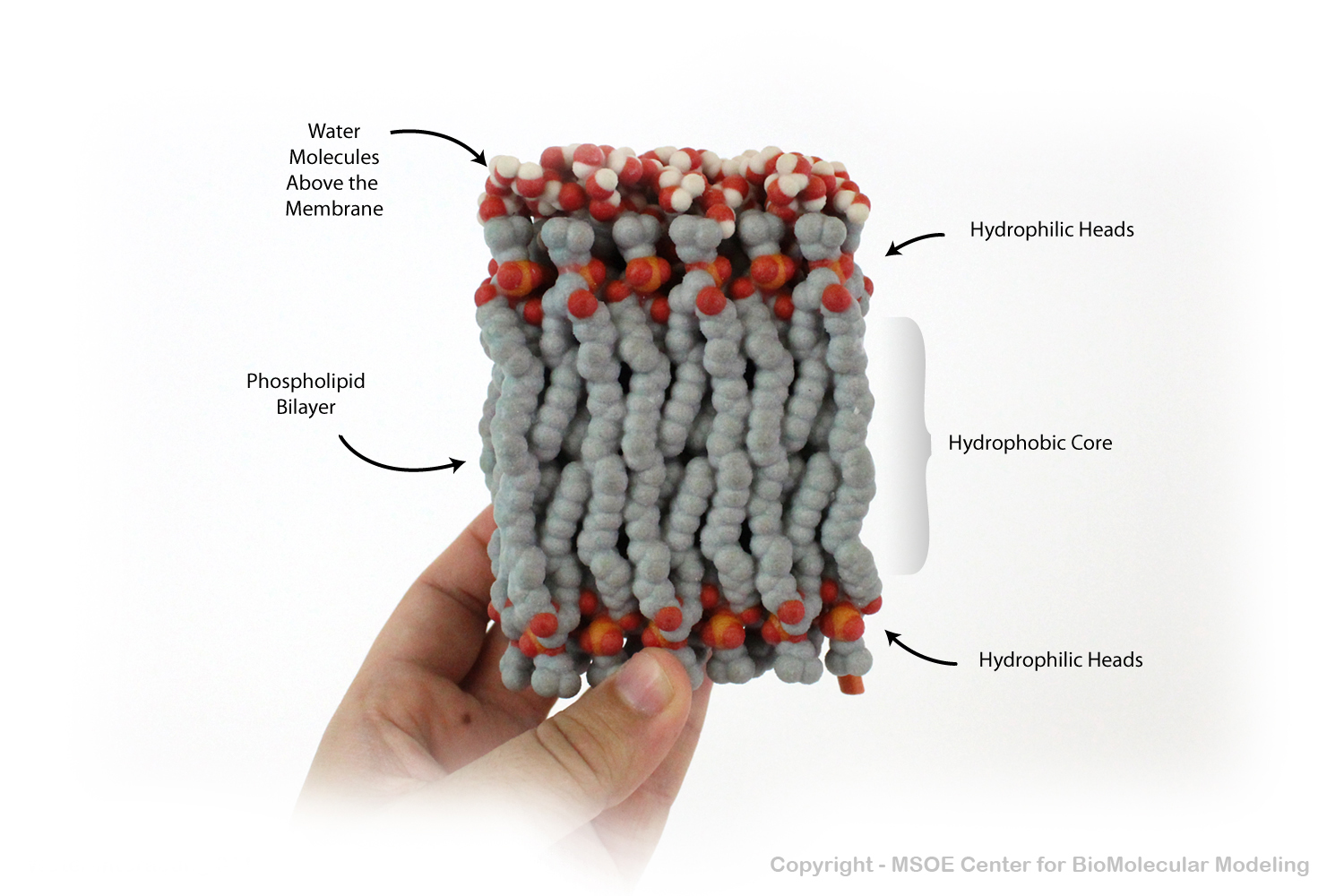
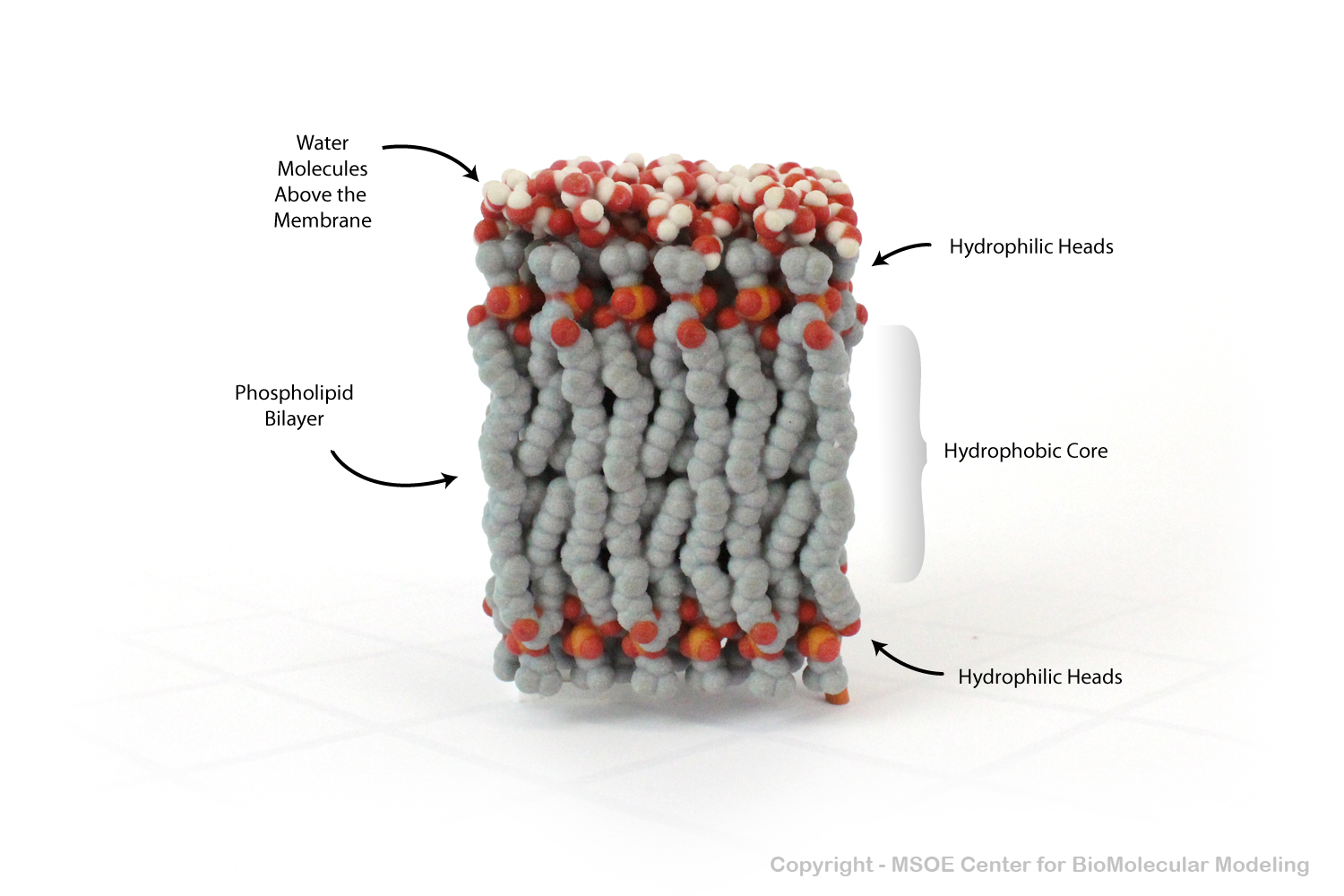
Phospholipid Bilayers (membranes) have a carbon-rich hydrophobic core that prevents polar water from crossing. In this model, water molecules are shown above the membrane, unable to pass to the bottom.
Phospholipid Bilayers (membranes) have a carbon-rich hydrophobic core that prevents polar water from crossing. In this model, water molecules are shown above the membrane, unable to pass to the bottom.
Phospholipid Bilayers (membranes) have a carbon-rich hydrophobic core that prevents polar water from crossing. In this model, water molecules are shown above the membrane, unable to pass to the bottom.


















